Google Bard is an AI-powered chatbot designed by Google. Bard uses natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning to simulate human conversation.
The chatbot is trained on a vast database of text, code, and images. Bard also has access to current information directly from the web.
This way, you can use Bard as a personal AI assistant to help with a number of tasks, such as replying to emails, writing marketing content, translating documents, summarizing meeting notes, and much more.
With Bard, Google has entered the rapidly growing generative AI market which is expected to reach USD 51.8 billion by 2028.
However, Google is not alone in the market. Other tools like ChatGPT and Microsoft Bing are competing with Bard to dominate the market. Such technology has the power to transform entire industries - marketing included, with AI tools like Surfer AI and ChatSonic.
In this article, we’ll go over everything you need to know about Google Bard, how to make the most of this chatbot, and alternative AI tools.
What is Google Bard?
Google Bard is an advanced, AI-powered conversational chatbot. Bard is powered by a new generation of large language models (LLM) that are trained on datasets of text, code, and images.
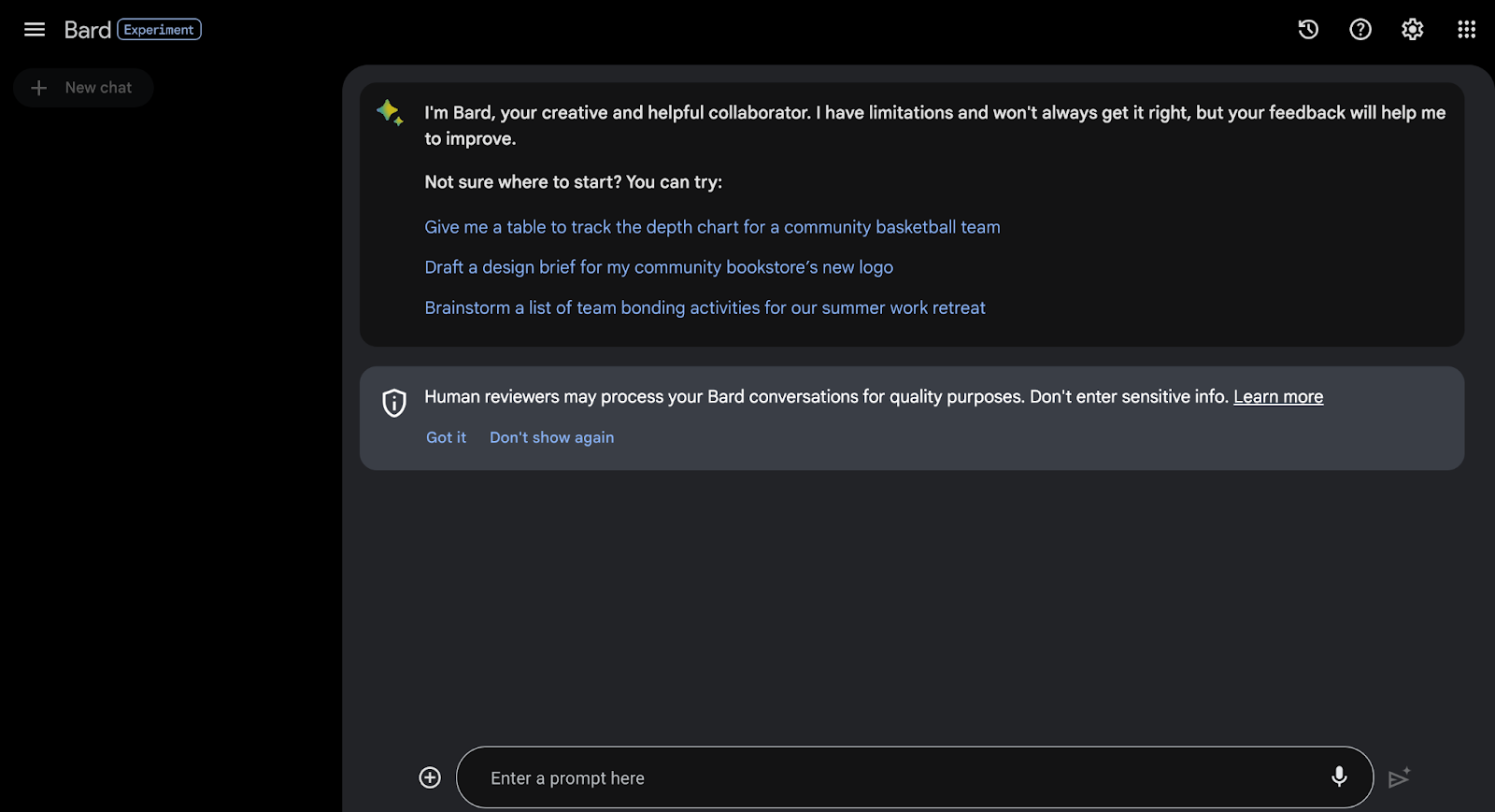
Google positions Bard as a helpful collaborator. You can type in a prompt and Bard will tap into current events and information from the web and come up with a structured answer.
This way Bard aligns with Google’s mission of making knowledge accessible and useful.
Among many use cases, Bard can help you:
- Generate different types of text formats like creative briefs, poems, code, scripts, and emails.
- Get answers to open-ended and challenging questions.
- Learn something new.
- Translate text.
For instance, you can ask Bard,
“What are the 6 Principles of Persuasion and how can I use them in my marketing campaigns?”

Bard’s response includes an explanation of the principles and ideas on how you can use them.
You can then ask Bard follow-up questions, such as to expand on one idea for a specific channel, or on a principle.
You also have the option to verify the answer by clicking on the Google it button to start a Google search, as well as to rate, modify, and export Bard's responses.
Bard is also available as an app on the Play Store and Apple Store.
When was Google Bard released
Google Bard was first released on February 2023, in a statement by the Alphabet and Google CEO, Sundar Pichai. That day, Bard opened up only to trusted testers.
A couple of weeks later, on March 21, 2023, Bard was released to the public in the US and UK. By July 2023, Bard became available in over 240 countries and territories and in more than 40 languages.
The release of Bard did not go without controversy.
In an example shared by Google, Bard shared false information, claiming that the James Webb Space Telescope took the first picture of an exoplanet.
Google used this opportunity to highlight that Bard is an experimental tool drawing on information from the web. So it might make mistakes.
That’s why, as with any AI language model, you should verify the information.
The chatbot is constantly learning and improving. So far, Bard has introduced nine updates. Some important updates include:
- April 2023: Bard can help you code in 20+ programming languages.
- May 2023: Google announced that Bard had adopted PaLM 2, a more advanced large language model. Bard is now available in three languages in over 180 countries.
- July 2023: Bard becomes available in over 40 new languages and expands in more countries, including all 27 EU countries and Brazil. You can now use Google Lens in Bard to upload images. Bard also gains text-to-speech capabilities in over 40 languages.
How does Google Bard work
Bard is powered by the Pathways Language Model 2 (PaLM 2), Google’s newest large language model. PaLM 2 is trained on a large dataset of text, code, and images.
This gives Bard the ability to understand the world better and handle advanced reasoning tasks, multilingual translation, and natural language generation.
Before switching to PaLM 2, Bard was initially powered by Google’s Language Model for Dialogue Applications (LaMDA).
Both language models function similarly; however, PaLM 2 is a newer, more efficient, and advanced AI version.
LaMDA was trained on a dataset of text and code, while PaLM 2 was trained on a dataset that includes text, code, and images.
Moreover, LaMDA is designed for dialogue-based applications, while PaLM 2 is designed for a wider range of tasks, including translation, writing, and coding.
This makes Bard with PaLM 2 more versatile and visual in its responses.
For example, you can ask Bard “What are some must-see video marketing campaigns of 2023?”.
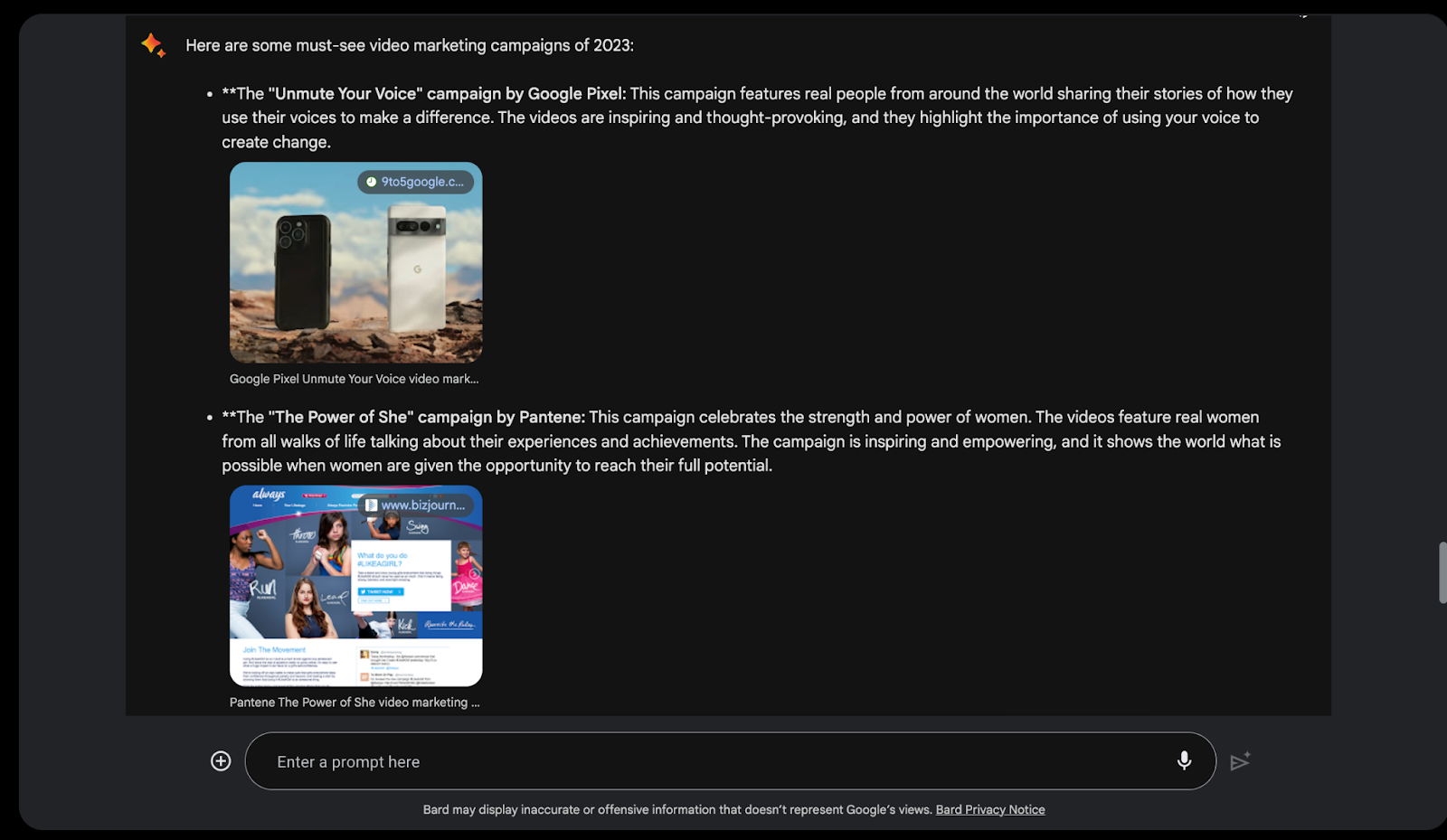
As you can see, you will get a visual answer.
Different from some other AI chatbots like ChatGPT that can only access information up to one point in time, Bard can tap into current information from the web.
Who is Google Bard for?
Bard is for everyone with a personal Google account that wishes to leverage the power of generative AI.
You can visit bard.google.com and sign up using your Gmail address.
Once you’re set up, you can start exploring Bard’s incredible capabilities and put this advanced AI chatbot to work for you.
Bard is now available to people in over 240 countries and territories and 40 languages.
People can use Bard to perform a number of tasks, like research, writing content, coding, and learning something new.
With Bard, Google aims to make knowledge further accessible and useful.
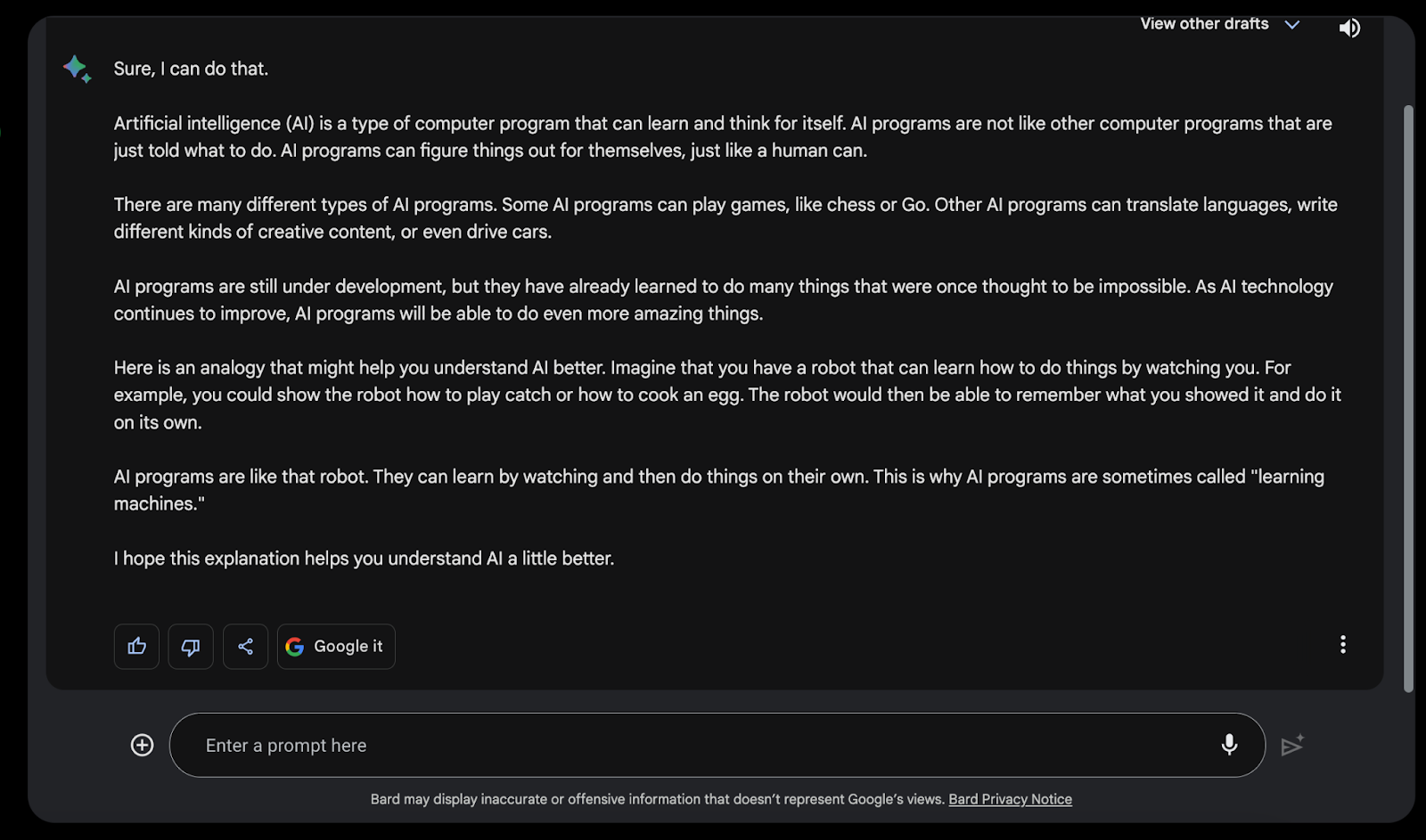
For example, you can use Bard to simplify complex topics.
Add a prompt like “Explain artificial intelligence to a 9-year-old / in simple language”
Bard will synthesize the information found across the web and give you an easy-to-digest answer - like the one below.
Something that sets Bard apart from other AI language models, is its ability to analyze images.
So for instance, you can upload a picture and ask Bard to write an Instagram caption for it or use it to summarize documents and notes.
For the best results, give Bard a bit of context in your prompts. The more information you feed it, the more usable and personalized its responses will be.

Bard can also help you write content, including cover letters, briefs, strategies, and emails.
In the example below, we’ve asked Bard to “Write a logo design brief for a small family cafe”.

You also have the option to directly export the Bard output to Gmail or Docs.

Is Google Bard reliable?
Google Bard is not always fully reliable. The chatbot is still an experiment, so it may provide inaccurate or misleading information.
These are known as AI hallucinations.
Bard learns by being exposed to data. When you interact with Bard, Google collects data on your conversation, usage information, and feedback.
You can give Bard a thumbs up or a thumbs down on each answer.
Google uses the data to improve and develop its products and machine learning technologies. So the more people that use Bard and provide feedback, the better the chatbot will get at giving correct information.
You can go around this limitation using the Google it bar inside Bard to start a Google search on the topic of your prompt.

As with any language model for dialogue applications, you will have to do your own fact-checking.
How much does Bard cost?
Google Bard is free. Everyone with a Google account can access it.
It’s likely that this service continues to remain free like most of Google’s mass services. Plus, the language model trains on usage data.
So the more people that use Bard, the smarter the chatbot will become.
Google Bard vs. ChatGPT
Both Bard and ChatGPT are conversational AI chatbots. So they have overlapping use cases and functionalities. ChatGPT was released in November 2022 by OpenAI, a couple of months before Bard. Both chatbots are powered by different language learning models.
Here are the main differences between the two:
Use cases
ChatGPT is trained on text data. Meanwhile, Bard is trained in text, code, and images. This makes Bard a more versatile tool with diverse use cases. You can upload images into Bard as well as expect visual answers. ChatGPT only accepts and returns text output.
Therefore, Bard is designed for a wider range of tasks than ChatGPT. ChatGPT is primarily designed for dialogue-based applications - even though it has found usage beyond it.
Moreover, Bard draws on current information from the web, while ChatGPT has only knowledge of information up to September 2021.
Functionality
Google Bard offers more functionalities than ChatGPT. Bard has the ability to process code and images besides text.
You can also, modify, rate, share, and export Bard’s output directly into Google Docs or Gmail. ChatGPT only allows you to rate its output.
Furthermore, Bard has an integrated Google it bar that allows you to easily check the factuality of its answers.
ChatGPT has both a free and paid version.
The paid version offers additional perks like faster response times, even during peak hours - the free web version is known to crash time after time.
Language models
Bard and ChatGPT are powered by different language models. Bard is powered by, PaLM 2, Google’s language model. This model is designed to perform a large number of tasks beyond providing conversation-style text answers.
Meanwhile, ChatGPT is a language model similar to InstructGPT, which is designed to interact in a conversational manner.
Google Bard vs. Microsoft Bing
Similar to Bard, Bing is a conversational AI chatbot that draws on information from the web to answer your questions.
Bing has incorporated the technology behind ChatGPT to leverage the engine’s search data.
Use cases
Bing works best in a question-and-answer format. Its aim is to provide information.
Similar to Bard, it also has the ability to pull real-time data from search. Bing’s newest version, is also positioned as an AI assistant, rather than simply a chatbot.
Functionality
Lately, Bing has been adding new functionalities, such as the possibility to upload images, use voice search, converse in different languages, and ask more complex questions.
These are all functionalities that Bard shares. Bard has a few additional functions such as the ability to export answers, pin, and share them.
Similar to Bard’s Google it button, Bing has its own fact-checking mechanism - the chatbot directly cites sources underneath each answer.
Language models
Bard uses Google's own language learning model, PaLM 2. Bing is powered by GPT-4, the same language model as ChatGPT.
Nevertheless, it has its own layer on top of it. Because different from ChatGPT and similar to Bard, Bing has access to information from search.
Google Bard alternatives
Google Bard is undoubtedly an impressive use of AI and generative language technology. Nevertheless, it’s not the only tool of its kind in the market.
There are various Google Bard alternatives out there that keep receiving continuous updates.
ChatGPT and Microsoft Bing are two of the alternatives that closely resemble Bard. Below we go into more detail about each of the mentioned Google Bard alternatives.
They all offer conversational support and assistance with various research and writing tasks.
Surfer AI
Surfer AI is a content writing tool that helps you create long-form content that ranks in search engines. It uses the same underlying generative AI model as ChatGPT 4.
The tool employs its own proprietary algorithm layered on training data, to analyze top ranking pages and write SEO content.
It takes about 20 minutes to create an article that includes relevant keywords and talking points for your topic.
ChatGPT
The web-based ChatGPT can be another alternative to Bard. The 3.5 version of the tool is free and it’s already being embraced in content marketing, academics, and research.
In fact, ChatGPT is the leading AI generative tool used for marketing purposes in the US according to Statista.
The downside of the free version of web-based ChatGPT is that it slows down when many people are using it. Plus, it has fewer functionalities compared to Bard, including a lack of visuals and exporting features.
What’s more, free ChatGPT’s knowledge is limited to things that have happened up to 2021.
Microsoft Bing
By partnering with OpenAI and leveraging ChatGPT's technology, Microsoft created Bing, a search-powered chatbot.
With it, users receive standard Bing search results and an answer generated by GPT-4. They can also interact with the AI and refine their search.
Lately, Microsoft Bing has introduced new AI features, such as being able to upload pictures in your search.
The addition of new features makes Bing more similar to Bard.
YouChat
YouChat is an AI chatbot positioned as a conversational search engine. The company aims to use AI to provide a better search engine experience.
The search engine can help you answer complex questions that require logical reasoning, code, and find recent information.
YouChat pulls its data from the web and presents it alongside links to the source. This way you can review the source and fact-check the responses.
To use YouChat, you need a Google account. There is both a free and paid version of it.
Jasper Chat
Jasper Chat is an AI chatbot copywriting tool built for driving business, sales, and marketing performance. The AI is focused on generating text specifically aimed at companies looking to create brand-relevant creative content.
Jasper Chat is not meant to be used as a search engine.
You can train Jasper on your brand by specifying the audience, or keywords in your prompts.
ChatSonic
ChatSonic, marketed as a "ChatGPT alternative with superpowers," is an AI chatbot powered by Google Search with an AI-based text and image generator.
Catering to business and marketing people, ChatSonic can help you generate text content like email, letters, blog posts, and AI art.
You can use the free web version or download the ChatSonic app to have it as a personal assistant on the go.
Key takeaways
- Google Bard is a versatile generative AI tool, that you can use as a personal assistant to research, write content, code, plan, and act as a multilingual translator.
- Bard is built on top of LaMDA and PaLM 2, two powerful natural language models that help the chatbot understand and generate natural language.
- Users from over 240 countries and territories can use Bard in over 40 languages.
- Bard is prone to AI hallucinations, meaning that it might produce incorrect or misleading information.
- There are a number of alternative language generative tools like Bard, including Surfer AI, ChatGPT, Microsoft Bing, ChatSonic and Jasper Chat.
Conclusion
Google Bard is making waves in the world of AI. Backed by Google’s powerful advancements and new discoveries in the field of artificial intelligence, Bard acts as your AI assistant.
The chatbot will answer questions and perform tasks by drawing on Google's real-time web information. This doesn't mean that Bard always produces accurate information.
As with any AI tool, you need to be aware of its limitations and stay tuned for new updates.
Also, Bard is not the only chatbot making headlines. Google is competing with other smart chatbots in the market, like ChatGPT, Bing Chat, ChatSonic, YouChat, and the like.
The rise of AI dialogue applications like Google Bard marks an exciting new era in the field of artificial intelligence.
These powerful tools have the potential to transform our lives, enabling us to engage with technology in more natural and intuitive ways. Nevertheless, there is a long way to go to building fully trustworthy AI systems.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect the adoption rate of Bard and other AI tools to grow, reaching even more users around the globe.

