A title tag determines how your web page will show up in search engine results pages (SERPs). Besides enticing the user to click on the page, it's a small but important ranking factor you shouldn't ignore.
This guide will teach you everything you should know about title tags and how to set them. We'll go over the best practices you should follow to optimize your tags properly and make every word count.
What you will learn
- What a title tag is and how it differs from an H1 tag and other commonly confused HTML elements.
- How title tags contribute to your search engine optimization (SEO) strategy.
- What to include in your title tags and how to structure them.
What are title tags in SEO?
A title tag is a piece of HTML code that defines a web page's title. Here's what it looks like:
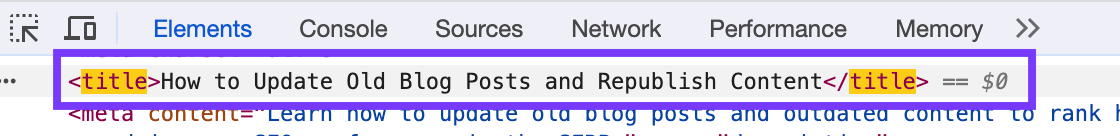
The title tag shows up as a clickable headline in SERPs, as well as browser tabs and link previews, so it must encapsulate the essence of the web page's content somehow.
While you can set a title tag at will, Google may rewrite it for SERPs to make it more relevant according to several factors like user intent and related searches.
With this in mind, setting a title tag mainly communicates your preference to Google, and the title might remain unchanged if you follow the necessary best practices, which we'll cover later in this guide.
Title tag vs. page title
Title tags are the same as page titles, so the difference is only semantic. Depending on your CMS, you may see a "page title" section, which indicates you should include the title you want to appear in SERPs.
Title tag vs. meta title
"Title tag" and "meta title" are also synonyms, and you may see a title tag referred to as an SEO title or SEO page title.
Title tag vs. H1
A title tag appears as a SERP headline, while an H1 tag shows up on the actual page as its main heading. Title tags and H1 tags can be identical or similar, but they shouldn't be too different.
Title tag vs. meta description
Meta descriptions show up under title tags in SERPs, and their main purpose is to provide a short summary of the page. It's important to align the meta description of web pages with the title tag to ensure relevance.
Why are title tags important?
Title tags are a notable SEO ranking factor, as confirmed by Google's John Mueller. While a title tag may not be a deal breaker when it comes to a page's SERP position, it helps search engines understand what the page is about.
If the page's content is accurately represented by the title tag, this gives you some valuable SEO points.
Of course, title tags aren't only meant for search algorithms. They influence various important metrics, such as:
- User experience
- Click-through rates
- Social sharing
Eye-catching title tags set your page apart in Google's search results and encourage readers to click on it.
With carefully optimized title tags and smart word choices, you can significantly boost your organic traffic.
Title tag examples
We showed you what a title tag looks like in the page's HTML code, now let's see how it appears on other places on the web.
Search results
The most important placement of a title tag is in the search results, where it looks like this:

In a sense, these clickable titles are the search results, and they define a user's first impression of your content. The page title must answer the search query precisely and be engaging enough to invite clicks.
Browser tabs
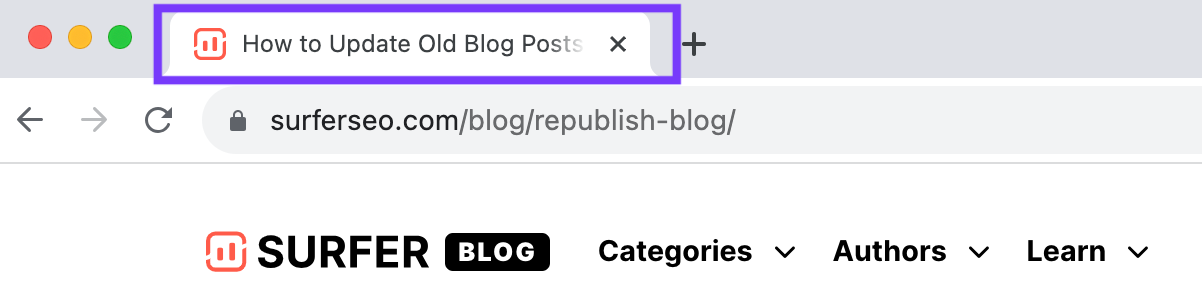
Users are sometimes confused when they see the browser tab displaying a title different from what they see on the page. That's because a browser tab shows the title tag, not the headline found in the body of content.
Here's what the title tag looks like in browser tabs:
Link previews
When you share something on social media or via messaging services, you'll almost always get a link preview. It typically contains a thumbnail alongside the page title, like so:
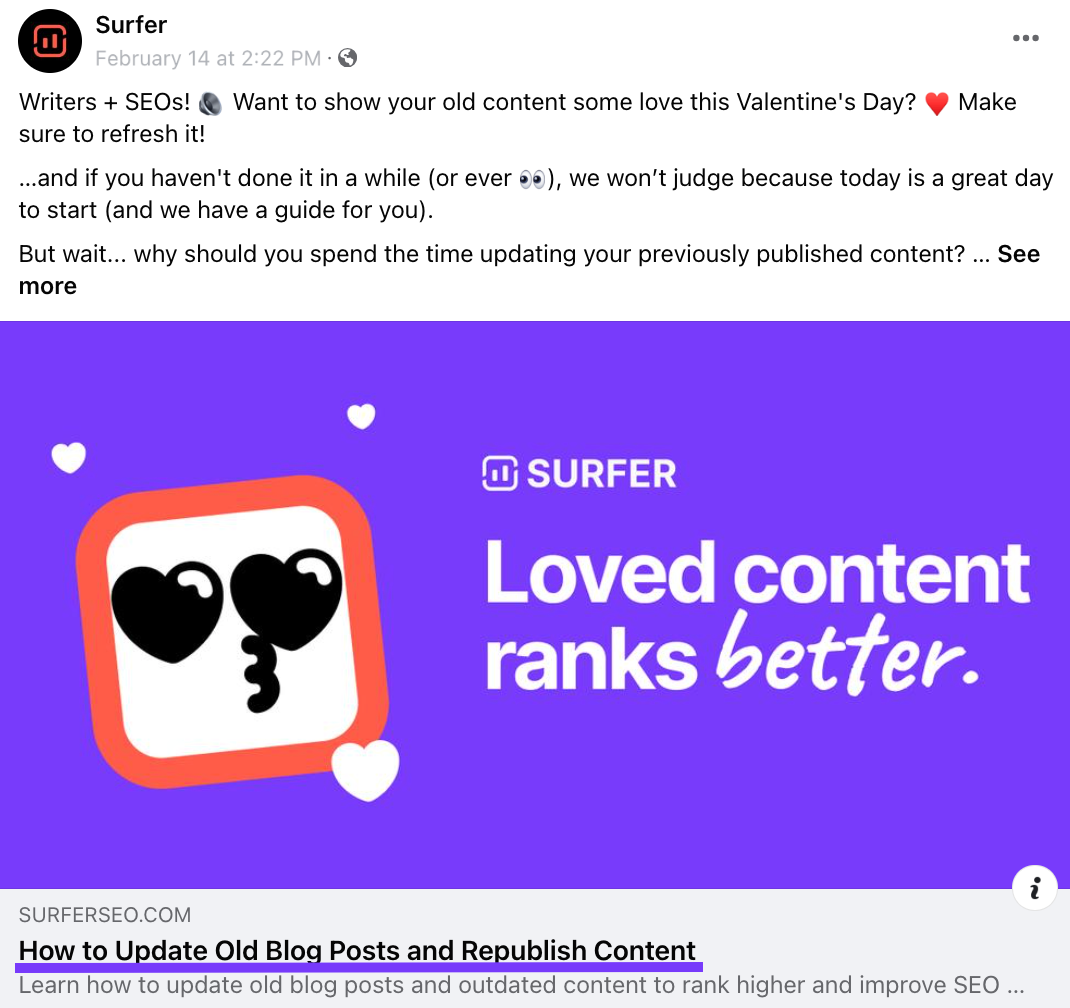
Much like with search results, title tags in link previews encourage clicks, so getting a page title right can boost traffic from several sources.
9 SEO title tag best practices
Writing good title tags isn't just about naming your page according to its content—there's more to it. Here are 9 best practices you can follow to write effective title tags.
1. Analyze the SERPs
When you select your core keyword, you must analyze the search results to understand the intent behind it. There are four types of search intent:
- Informational—The user is looking for high-level information about the topic/product
- Navigational—The user wants to reach a specific website
- Commercial—The user is in the later stage of their customer journey and is comparing different options
- Transactional—The user is looking to purchase the product
You can understand search intent by simply Googling your target keyword. For example, the search results for "on-page SEO" are mainly guides and tips, which indicates informational intent.
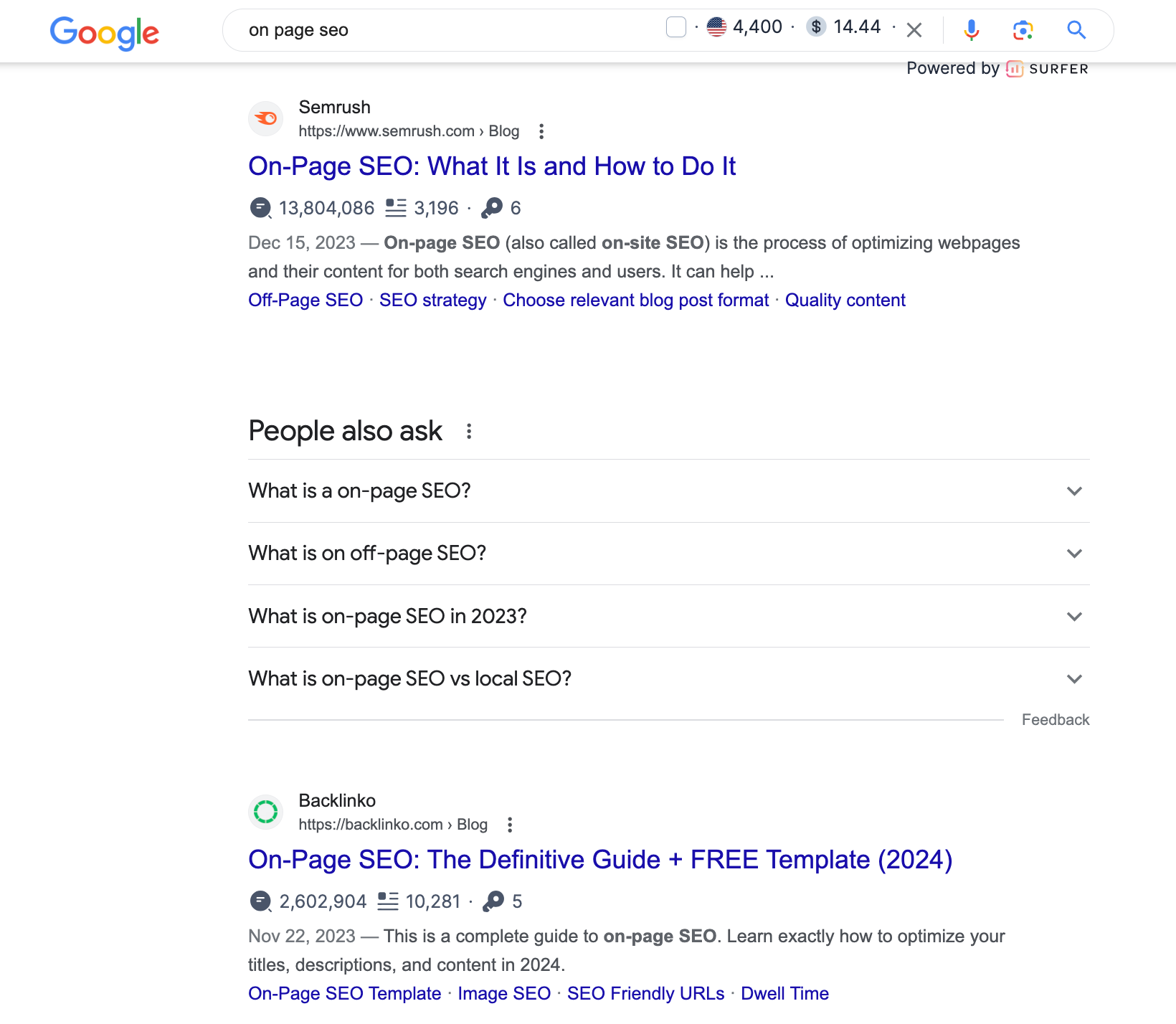
However, if you search for "on-page SEO software," you'll see product round-ups, so the intent is commercial.
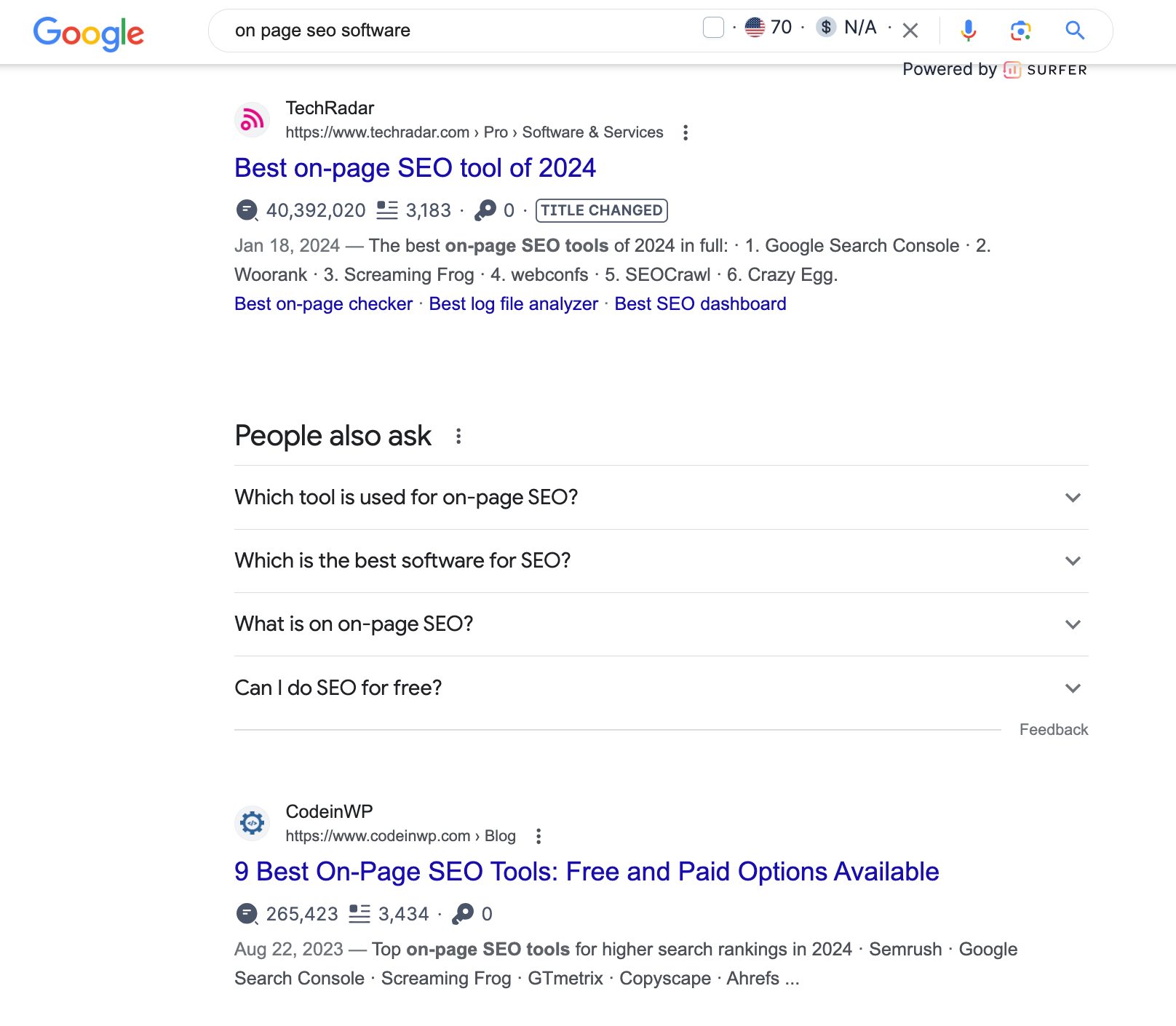
Understanding search intent helps you see which type of content you should create for the given keyword and how to reflect it in the title tag. You can draw inspiration for the title by examining the search results and your competitors, but make sure to create something unique instead of copying a title verbatim.
2. Target one main keyword
Your title tag should always focus on a single primary keyword. You'll most likely already know what that keyword is because you'll uncover it while doing keyword research before you start writing.
Let's say your main keyword phrase is "on-page SEO." In this case, it should be the focal point of the title tag with only a few additions that make the title engaging. For example, your title tag can be:
"Mastering On-Page SEO: A Complete Guide"
Now, this doesn't mean you shouldn't include any other keywords—just make sure to do it naturally. Keyword stuffing is one of the quickest ways to damage your SERP rank.
For example, if you have a shop selling water bottles in California, don't do this:
"Cheap Water Bottles | Water Bottles Shop California | Water Bottles in California"
Instead, do this:
"Best Cheap Water Bottles in California"
By using keywords naturally, you'll avoid SEO penalties while still being able to fit more than a single core keyword in your title.
3. Include important words first
A page's title tag must be compelling at first glance, so you need to pay attention to word order. The goal is to let the user see the most important words first, as doing so decreases the chances they'll scroll past your page.
Let's go back to our "on-page SEO software" example and assume you're writing a listicle and buying guide. In this case, you should avoid titles like this:
"Learn How To Choose the Best On-Page SEO Software"
Instead, go with something like this:
"Best SEO Software—Reviews + Buying Guide"
If you're unsure which words to place first, there's a simple rule to follow—focus on the main keyword and incorporate it at the front of your title tag.
4. Optimize title tag length
A title tag should be between 50 and 60 characters long. This includes spaces, so there's no room for waste—you must include all the relevant elements and phrases without fluff.
If your title tag exceeds the available space, it will cut off and won't be displayed properly on the search engine results page. Instead, the user will only see a part of it followed by an ellipsis, like so:
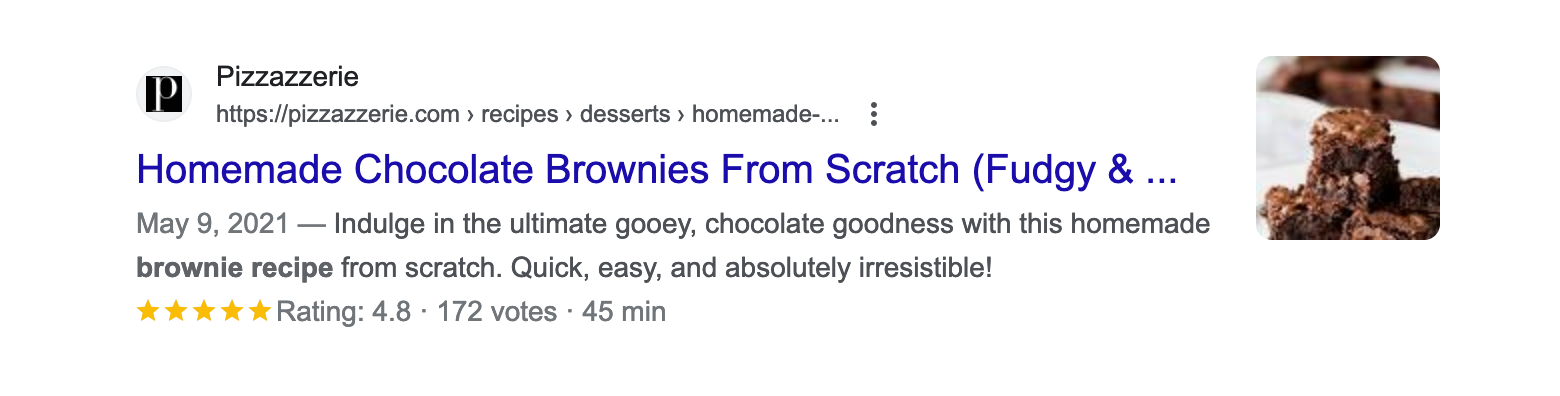
To avoid this, keep your title tags descriptive but concise. You might be compelled to add adjectives like in the above example to evoke a specific feeling and communicate a product's benefit, but keep them to a minimum. Stick to the page's core idea, and you can flower up the H1 more if needed.
5. Use title tag separators
Title tag separators like dashes, pipes, and colons are an excellent way to structure your title if you want to add short descriptions without damaging the title's effectiveness. They're also used to naturally add secondary keywords to the title and are particularly useful in e-commerce.
Here's an example of a well-implemented separator:
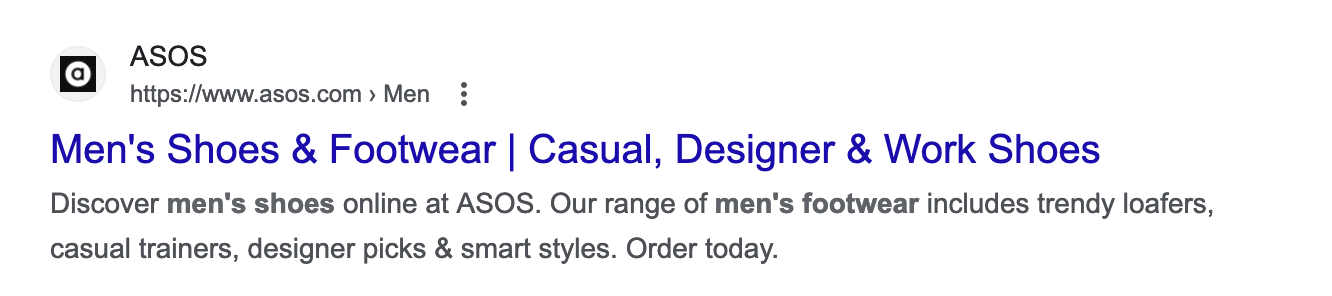
If it weren't for the pipe that separates categories from the main keyword, the title would look a bit jumbled.
As mentioned, the most important words shouldn't be placed so far in the title, so a separator helps maintain the right structure while still making the title descriptive and engaging.
6. Make the title similar to the H1 tag
As mentioned, Google rewrites title tags if it feels they could be better.
A study by Cyrus Shepard found that this can happen in a whopping 61.6% of cases. Upon further examination, the study concluded that similarities between a title tag and an H1 tag can drastically reduce the rewriting.
This makes perfect sense, as Google's algorithms care about consistency and an accurate representation of the page's contents. With that in mind, a good title tag should closely resemble the H1 that appears as the headline in the content's body.
Note that this doesn't mean your title tag and H1 tag must be identical - though it's no problem if they are. What matters is to include the core keyword in both and make sure the rest is similar enough. Take this title as an example:
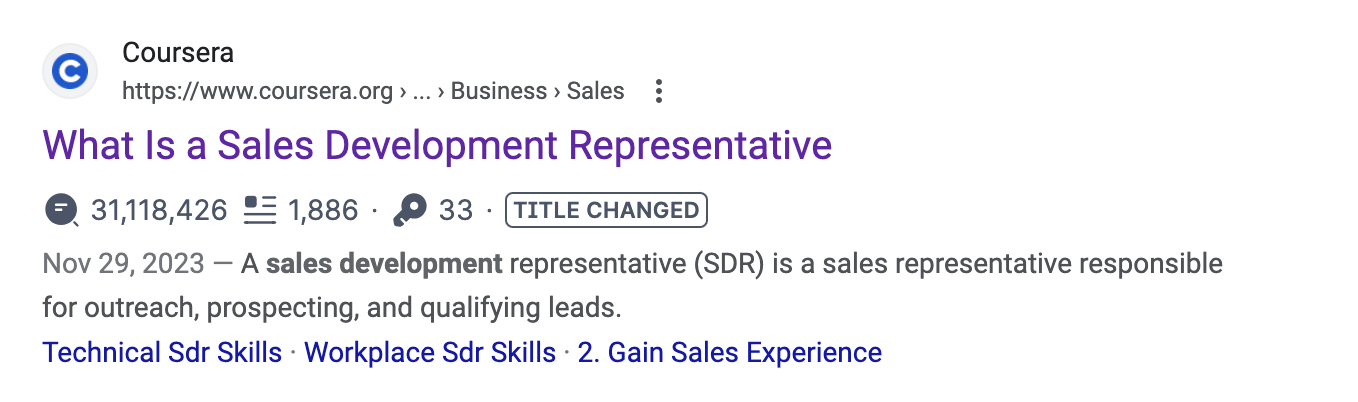
It doesn't precisely match the H1 tag.

Still, the tags are similar enough, which ensures the consistency that Google is looking for. So if you plan on making the title tag different from the H1, make sure there aren't significant differences between the two.
7. Write unique title tags
Each of your pages must have a unique title tag that matches the user's search intent. Otherwise, Google's algorithms may not know that the page is relevant, even if its content gives users what they need.
For example, if you're selling gardening supplies, it's okay to go with a broad title for the homepage or the page containing all your products. In that case, you can use something like:
"Buy High-Quality Gardening Supplies"
But when writing title tags for pages dedicated to specific products or categories, you shouldn't repeat this generic title. Instead, make sure to diversify your title tags according to the products so that both Google and users know exactly what the page is about, for example:
"Seed Starters — High-Quality Gardening Supplies"
8. Pay attention to word choice
You can only fit a handful of words in your title tags, so each one should be there for a reason.
While your titles should be concise, it doesn't mean they should be boring.
Make sure to include power words that evoke emotion and encourage action.
For example, if you write about tips for treating the common cold, don't go with a dull title like:
"A Guide to Treating the Common Cold"
Instead, do what Healthline did here:
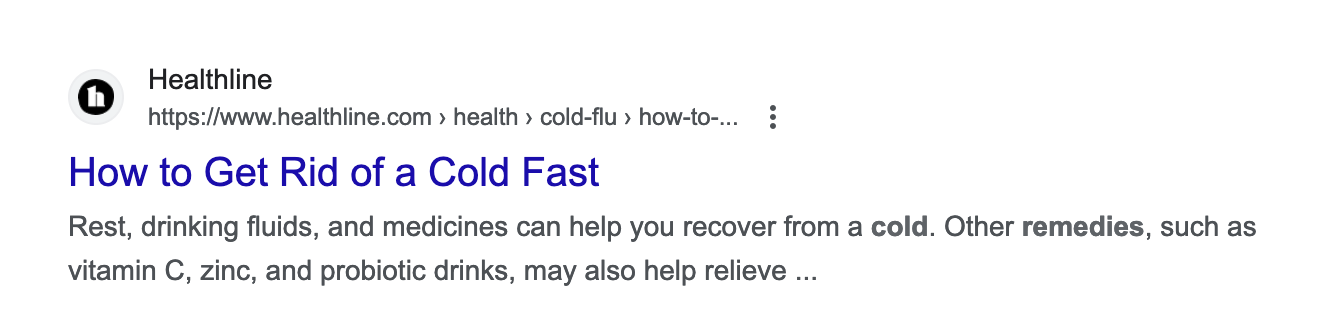
Healthline knows that readers want quick remedies, and the title reflects this. It also contains the main keyword and is concise enough to draw attention.
The power words you'll use mainly depend on your content's type or topic, but here are some universal examples:
- Ultimate
- Proven
- Must-have
- Instant
As a side note, don't overpromise when using power words. Nobody likes clickbait, so make sure your content delivers on the promise made in the title.
9. Follow a set title tag structure
Consistency is crucial for title tag optimization, as it promotes brand recognition. There's a high chance your pages will compete with countless others, so a bit of structure and familiarity can go a long way toward setting you apart from the crowd.
Whichever structure you choose, try to stick to it across your pages as much as possible. If you need some ideas, here are some common formulas:
- Primary keyword — Secondary keyword | Brand: Used Cars — Buy Used Vehicles in NYC | Cars.com
- Product — Category | Brand: Men's Slippers — Men's Footwear | Nike
- Category | Specific products | Brand: Women's Tops | Shirts, Sweaters, & Cardigans | Zara
Note that the brand name isn't mandatory, but it's beneficial for standing out among other search results. This is particularly important if you run an e-commerce store, as the user will likely see many page titles that look pretty much the same.
If you can add the brand name without exceeding the character limit or omitting important keywords, go for it.
Nailing the right title tag structure might take some experimenting, so play around with a few options to see what works best. You can track your page's rankings and performance using Google Search Console, so do some A/B testing until you zero in on the best structure.
Key takeaways
- A title tag is an HTML element that determines your page's title in SERPs, link previews, and browser tabs. It's not the same as an H1 tag, which is displayed as the headline on the page itself.
- Title tags are important for two reasons—Google considers them a ranking factor, and they have the power to draw a reader's attention and boost your click-through rate and traffic.
- When writing a title tag, focus on a specific keyword and analyze the SERPs to understand its search intent. Doing so helps you create the type of content that matches the intent and gives users what they're looking for.
- Important words should be placed at the front of a title tag, followed by other elements like the secondary keyword, short description, category, and/or brand name.
- You can use separators to structure your title tags and implement the necessary keywords naturally. When you decide on a structure, stick to it across your pages to ensure consistency.
- Your entire title tag must fit into 60 characters, including spaces, so there's no room for fluff. Stick to keywords, power words, and other elements that will make your title compelling.
Conclusion
A title tag might seem like a small piece of the SEO puzzle, but don't underestimate its impact. A well-written title can make a world of difference to your organic traffic and improve your SERP rank, so make sure it accurately represents your page.
By adhering to the best practices outlined in this guide, you'll be well on your way to creating compelling title tags, that not only rank well but also entice clicks.

